BECE 2006 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. The property of a rock that makes it different from water is that it has
Solution: Water is a liquid that takes the shape of its container, while a rock (solid) maintains a fixed shape regardless of its container.
2. A plane mirror can be described as opaque because it
Solution: Opaque materials do not allow light to pass through. Mirrors are opaque because they reflect nearly all incident light.
3. Wood is used to make the handles of cooking utensils because it is a
Solution: Wood's low thermal conductivity prevents heat transfer from the hot utensil to the hand, reducing burns.
4. Ventilation holes are made at the upper part of a door to allow air to rise by
Solution: Warm air rises due to convection, so upper vents facilitate hot-air escape and cool-air intake below.
5. When the north poles of two magnets are brought together they
Solution: Like magnetic poles (north-north or south-south) repel each other according to fundamental magnetic laws.
6. A fuse is used in an electrical circuit to
Solution: Fuses contain a wire that melts during overcurrent, breaking the circuit to prevent appliance damage.
7. The angle between an incident ray and a reflecting surface is 20°. Determine the angle of reflection.
Solution: Angle of incidence is measured from the normal. Here, 90° - 20° = 70° is the angle of incidence, and reflection equals incidence.
8. A screw is a machine which works in the same way as
Solution: A screw's threads act as a spiraled inclined plane, converting rotational force into linear motion.
9. Power is defined as the rate at which
Solution: Power (watts) = energy (joules) / time (seconds), making it the rate of energy consumption.
10. An example of a lever in which the effort is applied at the middle is a
Solution: Forceps are third-class levers where effort (applied at the middle) lies between fulcrum (end) and load (tips).
11. A simpler way of maintaining the efficiency of a machine is by
Solution: Lubrication reduces friction between moving parts, minimizing energy loss and wear.
12. The part of a seed which grows to become the shoot of a plant is the
Solution: The plumule is the embryonic shoot that develops into the stem and leaves after germination.
13. One disease that affects the nervous system of humans is
Solution: Poliomyelitis (polio) is caused by a virus that attacks motor neurons in the spinal cord.
14. Which of the following life processes leads to the release of energy?
Solution: Cellular respiration breaks down glucose to release ATP (energy) in cells.
15. Mineral salts in dead organisms are released into the soil by a process called
Solution: Decomposers (e.g., bacteria) break down dead matter, recycling minerals like nitrogen and phosphorus into the soil.
16. Spectacles fitted with concave lenses are worn by people suffering from
Solution: Concave lenses diverge light rays, correcting myopia (short-sightedness) by focusing light onto the retina.
17. Which of these organs in humans releases carbon dioxide as a waste product?
Solution: Lungs expel CO₂ (a respiratory waste product) during exhalation.
18. Farmers do not plant the stems of maize because the stems
Solution: Maize stems lack nodes/buds needed for vegetative propagation; maize is grown from seeds or cobs.
19. Which of the following ways of treating water makes the water soft?
Solution: Washing soda (sodium carbonate) removes calcium/magnesium ions, converting hard water to soft water.
20. Water that needs a small amount of soap to form lather is described as
Solution: Soft water lacks Ca²⁺/Mg²⁺ ions, allowing soap to lather easily with minimal quantity.
21. Common salt (sodium chloride) is obtained from sea water by
Solution: Solar evaporation of seawater leaves behind salt crystals in salt pans.
22. The chemical formula of a compound describes the
Solution: Formulas like H₂SO₄ show elemental ratios (2H:1S:4O), not bonding or molecular count.
23. Which of the following solvents can be used to remove grease from the hand?
Solution: Turpentine (organic solvent) dissolves nonpolar grease, unlike water or palm oil.
24. How many different elements are present in the compound \( H_2SO_4 \)?
Solution: H₂SO₄ contains hydrogen (H), sulfur (S), and oxygen (O) — three distinct elements.
25. Producers in an ecosystem are plants that
Solution: Producers (autotrophs) synthesize food via photosynthesis, forming the base of food chains.
26. The disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite is
Solution: Plasmodium (transmitted by mosquitoes) causes malaria, characterized by fever and chills.
27. Vaccination is carried out to
Solution: Vaccines stimulate white blood cells to produce antibodies, providing adaptive immunity.
28. Which of the following farming practices is likely to make the soil poor in nutrients?
Solution: Burning destroys organic matter and nutrients (like nitrogen), reducing soil fertility.
29. The type of cloud found closest to the earth’s surface is
Solution: Stratus clouds form below 2,000 meters, often appearing as low-lying gray sheets.
30. The amount of water vapour in the atmosphere is called
Solution: Humidity quantifies atmospheric water vapor, affecting weather and comfort.
31. The planet which is farthest away from the sun is
Solution: Pluto (dwarf planet) has the largest orbital radius in the solar system, ~39.5 AU from the Sun.
32. Which of the following gases is involved in the process of rusting?
Solution: Rusting (iron oxidation) requires oxygen (\(4Fe + 3O_2 + 6H_2O \rightarrow 4Fe(OH)_3\)).
33. A non-reactive metal can be identified from other metals because its surface is
Solution: Noble metals (e.g., gold) resist oxidation, retaining a shiny surface unlike reactive metals that tarnish.
34. The property to a metal that makes it possible for it to be drawn into a wire is called
Solution: Ductility allows metals to be stretched into wires without breaking (e.g., copper wiring).
35. The main reason why food is processed is to make it
Solution: Processing (e.g., canning, drying) primarily extends shelf life by inhibiting microbial growth.
36. The process by which kerosene rises up in the wick of a lantern is known as
Solution: Capillary action draws liquid up narrow tubes (like wick fibers) against gravity via adhesion/cohesion.
37. Which of the following statements about friction is not true?
Solution: Friction opposes motion (reducing speed), generates heat, and causes wear; it never increases speed.
38. Arteries are blood vessels which carry
Solution: Arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to tissues (except pulmonary artery).
39. Which of the following structures is not involved in blood circulation?
Solution: Muscles facilitate movement but aren't part of the circulatory system (heart pumps, vessels transport).
40. A substance of mass 10 kg has a density of 2.0 kg m\(^{-3}\). Calculate its volume.
Solution: Density = mass/volume → volume = mass/density = 10 kg / 2 kg/m³ = 5 m³.
1. Question 1
1. (a) The diagram below shows the electrical method of magnetizing a nail.
Study the diagram and use it to answer the questions that follow.
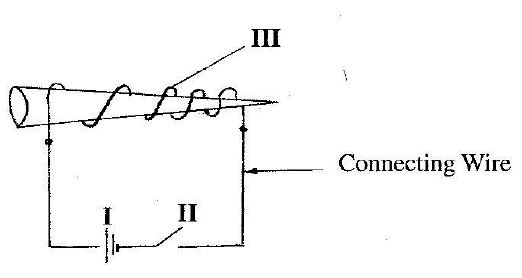
(i) Give the names of the parts of the circuit labelled I, II and III.
(ii) List two substances that can be made into a magnet.
(iii) State two other methods of making magnets.
(iv) Name one material that is used in making an electrical wire.
(v) Give two properties of the material you named in (iv) which makes it useful as a wire.
(b) The diagram below shows the set-up for the preparation of carbon dioxide in the laboratory.
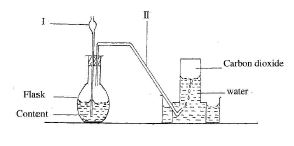
(i) Name the parts of the set-up labelled I and II.
(ii) Give the name of the method of gas collection shown in the diagram.
(iii) Give one property of gases collected over water.
(iv) What will happen if component I does not dip into the contents of the flask?
(v) List two compounds that form the content of the flask.
(vi) Write down the systematic name of carbon dioxide.
(c) In an experiment, yam pap is put into two test tubes A and B containing iodine solution. The test tubes are warmed slightly to a temperature of 37°C and saliva is put into test tube B.
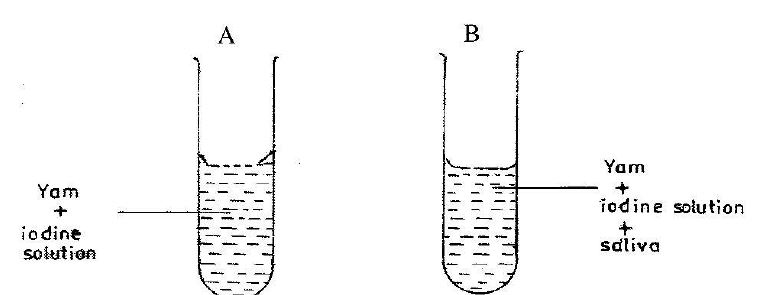
(i) State the colour of the content of test tube A.
(ii) State the colour changes of the contents in test tube B after about 3 minutes.
(iii) Fehling’s solution is added to the contents of test tube B after the 3 minutes and it turns brick-red. What food substance is present?
(iv) Give two functions of saliva in eating.
(v) Why was it necessary to warm the contents of the test tubes to about 37°C?
(vi) Give two aims of the experiment.
Solutions for Question 1
1. (a) (i) I - Cell; II - Key or switch; III - Solenoid or coil.
(ii) Iron (Fe), Steel, Nickel (Ni), Cobalt (Co).
(iii) Single stroking, Double stroking, Induction, Hammering.
(iv) Copper (Cu), Aluminum (Al), Steel, Iron (Fe), Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Platinum (Pt).
(v) Ductile, Malleable, Low resistivity, High tensile strength.
1. (b) (i) I - Thistle funnel; II - Delivery tube.
(ii) Upward delivery or downward displacement of water.
(iii) Insoluble in water; Less dense than water.
(iv) The gas produced will escape through the thistle funnel.
(v) Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃), Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Calcium chloride (CaCl₂), Water (H₂O).
(vi) Carbon (IV) oxide.
1. (c) (i) Blue black.
(ii) Pale blue black.
(iii) Maltose or reducing sugar.
(iv) - Makes food softer for easier chewing/swallowing.
- Contains enzyme ptyalin that breaks down carbohydrates to reducing sugar.
(v) To attain normal body temperature for efficient enzyme activity in saliva.
(vi) - Show saliva digests carbohydrates/starch.
- Show carbohydrate digestion starts in the mouth.
- Show yam contains starch.
2. Question 2
2. (a) (i) State two conditions that are required for photosynthesis to take place.
(ii) How would you show that starch is formed during photosynthesis?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation to show the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen.
(c) (i) What is a satellite?
(ii) Give one example of a natural satellite.
(iii) List two uses of artificial satellites.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2. (a) (i) Water, Carbon dioxide, Chlorophyll, Light.
(ii) - Pluck a leaf exposed to sunlight for 3+ hours.
- Boil leaf to kill cells/stop photosynthesis.
- Place in warm alcohol to remove chlorophyll.
- Rinse in warm water and add iodine solution.
- Blue-black color indicates starch presence.
2. (b) \( 2H_2 + O_2 \rightarrow 2H_2O \)
2. (c) (i) A heavenly body that orbits a larger one.
(ii) Moon (Earth's satellite), Planets (Sun's satellites).
(iii) Weather forecasting, Telecommunication, TV signal transmission, Space photography, Internet networking, GPS navigation.
3. Question 3
3. (a) Define:
(i) self-pollination
(ii) cross-pollination
(b) State two ways in which cross-pollinated plants are better than self-pollinated plants.
(c) Sodium chloride is prepared by the reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.
(i) Write a balanced equation for the reaction.
(ii) What is the name given to this reaction?
(d) Describe an experiment to show that pressure acts in all directions in a liquid.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3. (a) (i) Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of the same flower.
(ii) Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of another plant of the same species.
3. (b) - Produces disease-resistant offspring.
- Yields stronger/healthier offspring.
- Causes genetic variations for better adaptation.
3. (c) (i) \( HCl + NaOH \rightarrow NaCl + H_2O \)
(ii) Neutralization reaction.
3. (d) - Make holes of equal size at same height around a container.
- Fill container with water.
- Water jets out equally in all directions.
- Demonstrates equal liquid pressure in all directions.
4. Question 4
4. (a) (i) What is a vector of a disease?
(ii) State two methods each to destroy vectors of:
(a) River blindness;
(b) Malaria.
(b) Write systematic names of:
(i) CaCO₃
(ii) FeS
(iii) NaCl
(iv) NaOH
(c) (i) Give two properties common to all states of matter.
(ii) A stone (mass 60 g) raises water level from 60 cm³ to 75 cm³. Calculate its density.
Solutions for Question 4
4. (a) (i) Agent carrying disease-causing organisms.
(ii) (a) River blindness:
- Spray chemicals to kill black flies.
- Clear bushes along rivers to destroy breeding grounds.
(b) Malaria:
- Spray insecticides indoors/outdoors.
- Clear choked gutters/stagnant water.
- Use insecticide-treated nets.
- Pour oil on stagnant water to kill larvae.
- Introduce larva-eating fish in ponds.
4. (b) (i) Calcium trioxocarbonate(IV)
(ii) Iron(II) sulphide
(iii) Sodium chloride
(iv) Sodium hydroxide
4. (c) (i) Has mass; Occupies space (volume).
(ii) Volume = 75 cm³ - 60 cm³ = 15 cm³; Density = 60 g / 15 cm³ = 4 g/cm³.
5. Question 5
5. (a) Mention five differences between plants and animals.
(b) Define (with example):
(i) compound
(ii) element
(c) (i) Give two differences between electrical insulators and conductors.
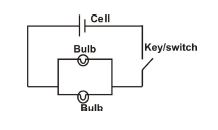
(ii) Draw and label a circuit: cell + switch + two bulbs in parallel.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
5. (a)
| Plants | Animals |
|---|---|
| Make own food (photosynthesis) | Cannot make own food |
| Immobile (fixed position) | Mobile (free movement) |
| Slow response to stimuli | Fast response to stimuli |
| Cell wall present | No cell wall |
| Store excess carbs as starch | Store excess carbs as glycogen |
| Absorb CO₂/release O₂ | Inhale O₂/exhale CO₂ |
| Permanent vacuoles | Temporary vacuoles |
| Growth at specific regions | Growth throughout body |
5. (b) (i) Compound: Substance from ≥2 elements in fixed ratio (e.g., NaCl, H₂O).
(ii) Element: Substance of one atom type (e.g., Iron, Oxygen).
5. (c) (i)
| Insulator | Conductor |
|---|---|
| No free electrons | Free electrons enable conduction |
| High resistance | Low resistance |
| No forbidden band gap | Forbidden band gap present |
(ii) Circuit diagram: